DataScience Blog
R Part- 4
April 25, 2020
Here we go with next set of commands. In this page we will see datatype conversion. As we are going to handle with different types of data and we should also know how to convert from one type to another. Here we go!
R has many datastructures. It includes
- Vector
- List
- Matrix
- Data Frame
- Factors
-
Tables
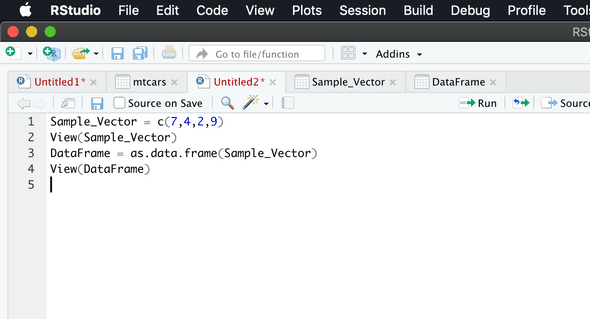
Now let us see how to do conversionConverting Vector to Data Frame
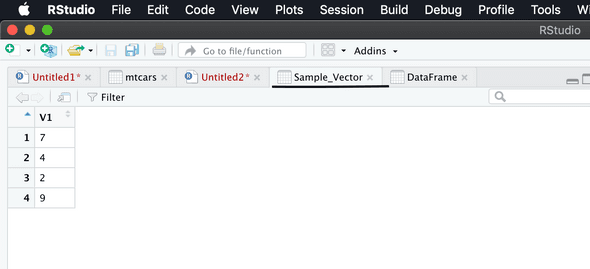
SampleVector = c(7,4,2,9)
View(SampleVector)
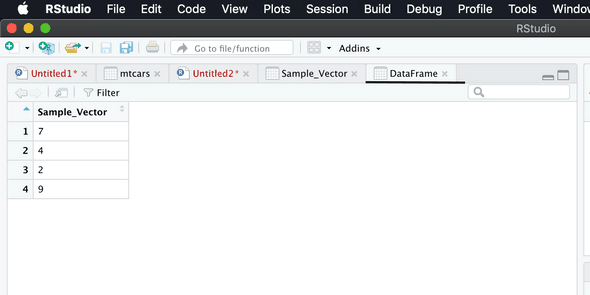
DataFrame = as.data.frame(Sample_Vector)
View(DataFrame)Output for above commands in screenshot
 Now we will see how to convert from numeric to factor, numeric to categorical, categorical to numeric,
Now we will see how to convert from numeric to factor, numeric to categorical, categorical to numeric,Numeric to Factor conversion
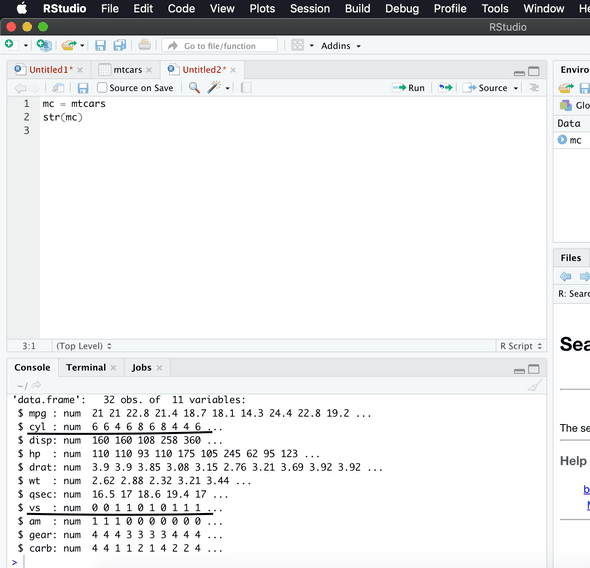
mc = mtcars
str(mc)
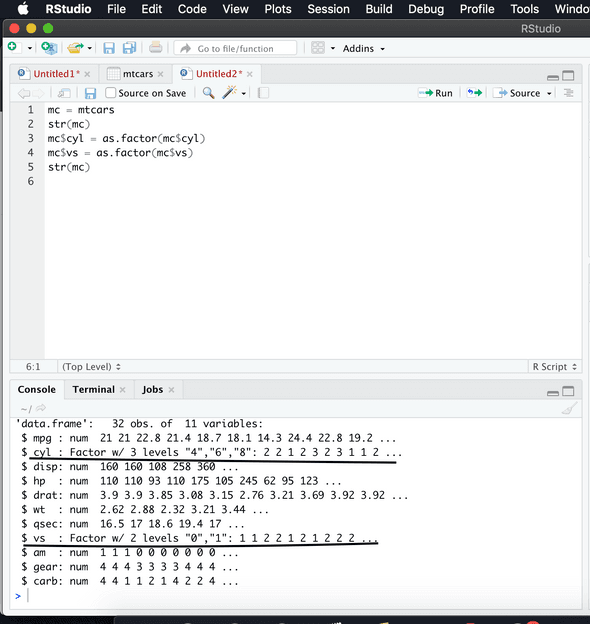
mc$cyl = as.factor(mc$cyl)
mc$vs = as.factor(mc$vs)
str(mc)Output for above commands in screenshot
Numeric to Categorical conversion
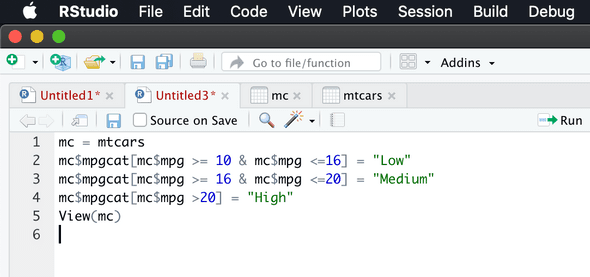
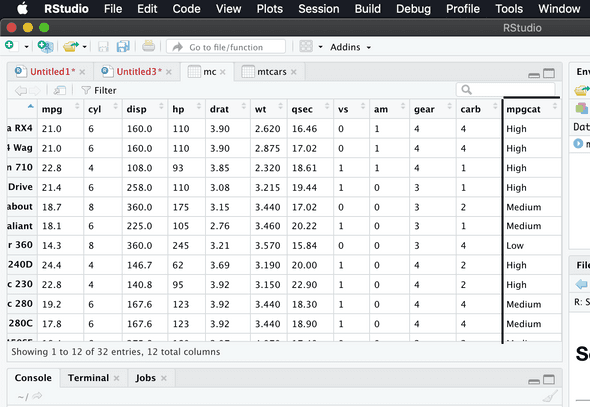
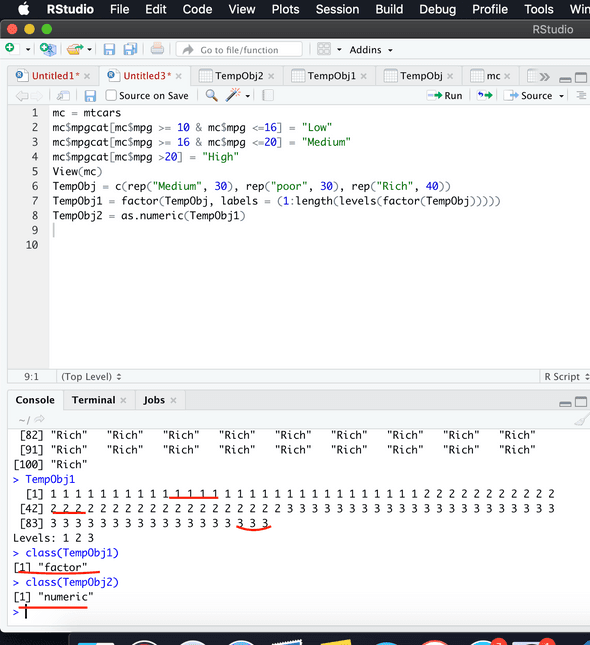
mc$mpgcat[mc$mpg >= 10 & mc$mpg <=16] = “Low”
mc$mpgcat[mc$mpg >= 16 & mc$mpg <=20] = “Medium”
mc$mpgcat[mc$mpg >20] = “High”Output for above commands in screenshot
Categorical to Numeric Conversion
TempObj = c(rep(“Medium”, 30), rep(“poor”, 30), rep(“Rich”, 40))
TempObj1 = factor(TempObj, labels = (1:length(levels(factor(TempObj)))))
TempObj2 = as.numeric(TempObj1)Output for above commands in screenshot
With this we will end up R, From next, we will start with Python. I will also check out for missed commands in R and update in middle, meanwhile lets start to learn python!!!!